Welcome to STA 199
Lecture 1
Dr. Elijah Meyer
Duke University
STA 199 - Summer 2023
May 17th, 2023
Welcome

Goals for Day 1
Get organized
- Get to know the professor
- Get to know each other
- Course overview
- Register with GitHub & Slack (if you haven’t already)
- Go over R + R-studio
- Start making visualizations
Who Am I?



Who Are You?
Please share with your neighbors:
- Major
- Year
- Why you are taking this course
- Anything else
What is data science?
What is data science?
“Data science is a concept to unify statistics, data analysis, machine learning and their related methods in order to understand and analyze actual phenomena with data. It employs techniques and theories drawn from many fields within the context of mathematics, statistics, information science, and computer science.”
Examples of data science
- Identification and prediction of disease
- Targeted advertising
- Supply chain optimization
- Sports recruitment + strategist
- The list goes on and on…..
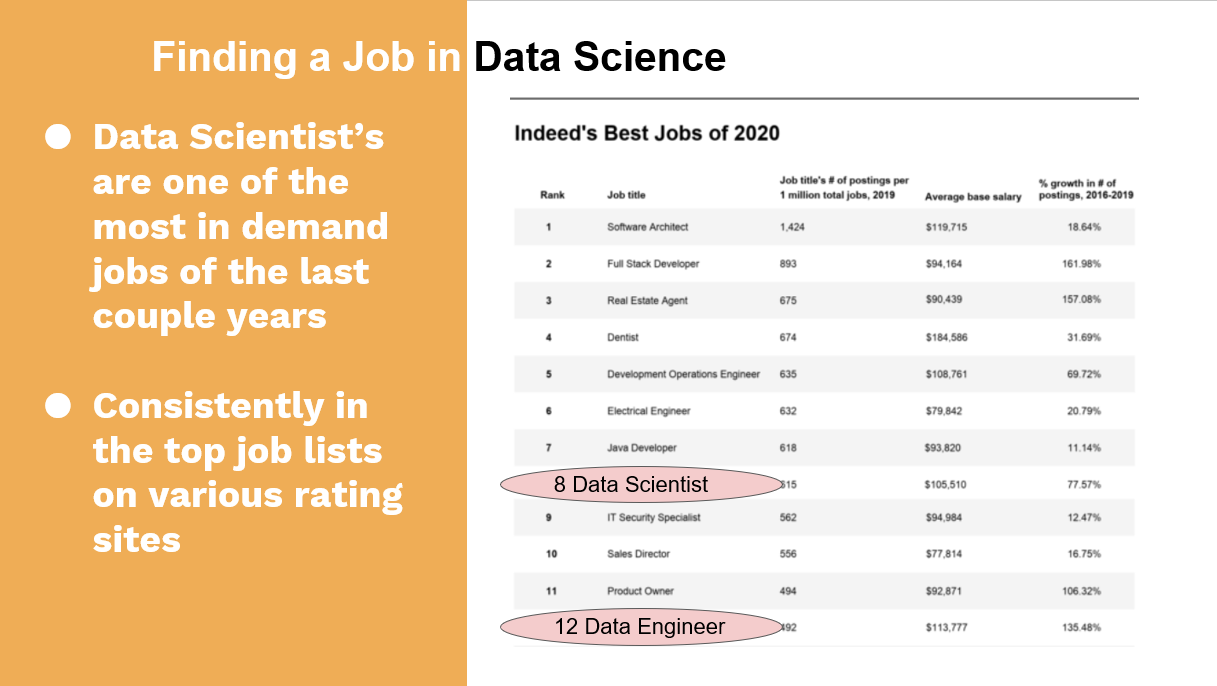
Jobs

Jobs

Jobs
Data literacy
Our Course
Our Classroom
- Community
- Communication
- Respect
Course objectives
Learn to explore, visualize, and analyze data in a reproducible and shareable manner
Gain experience in data wrangling, exploratory data analysis, predictive modeling, and data visualization
Work on problems and case studies inspired by and based on real-world questions and data
Learn to effectively communicate results through written assignments and final project presentation
Some of what you will learn
– Fundamentals of R
– Data visualization
– Version control with GitHub
– Reproducible reports with Quarto
– Regression
– Statistical inference
R - figures
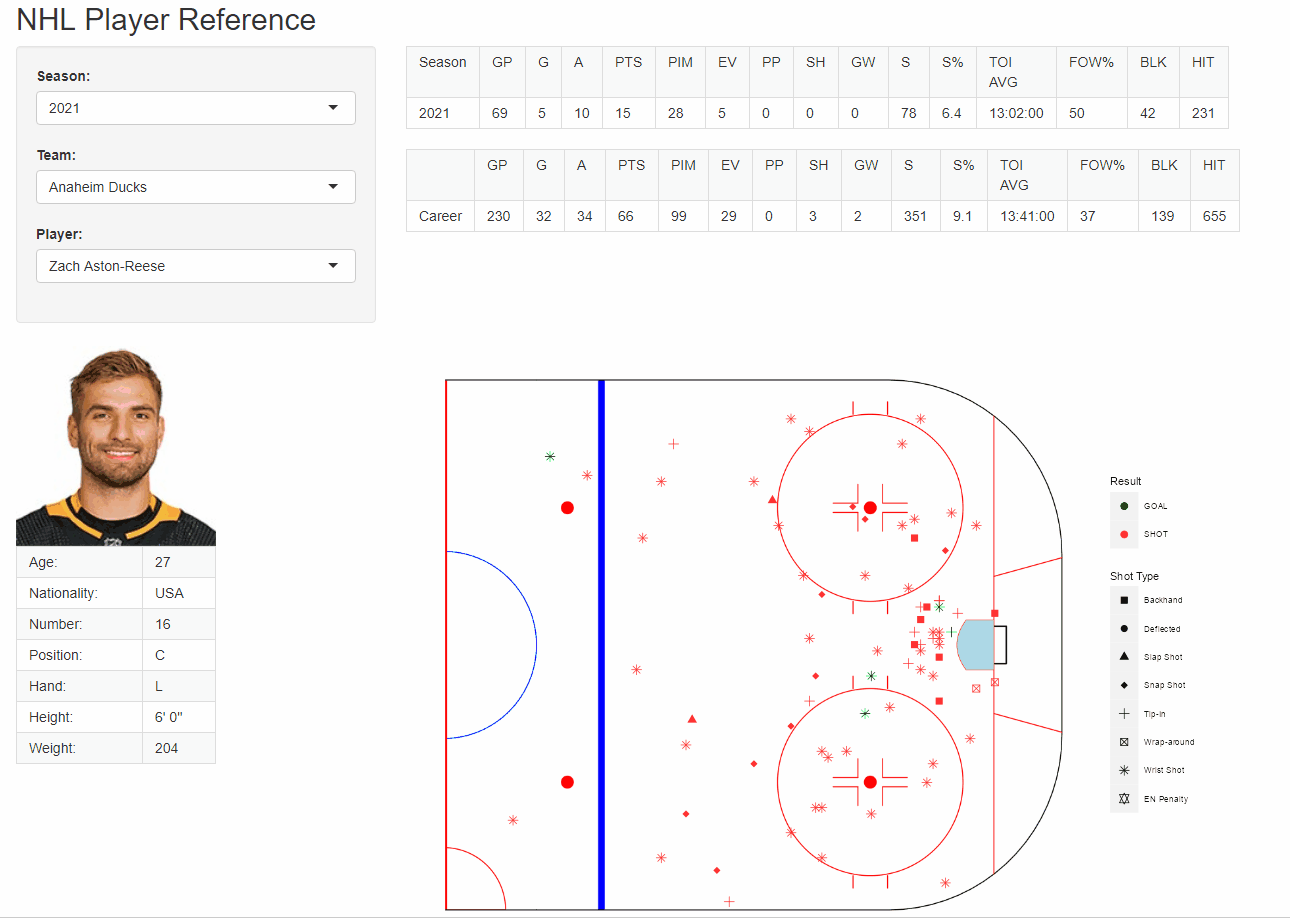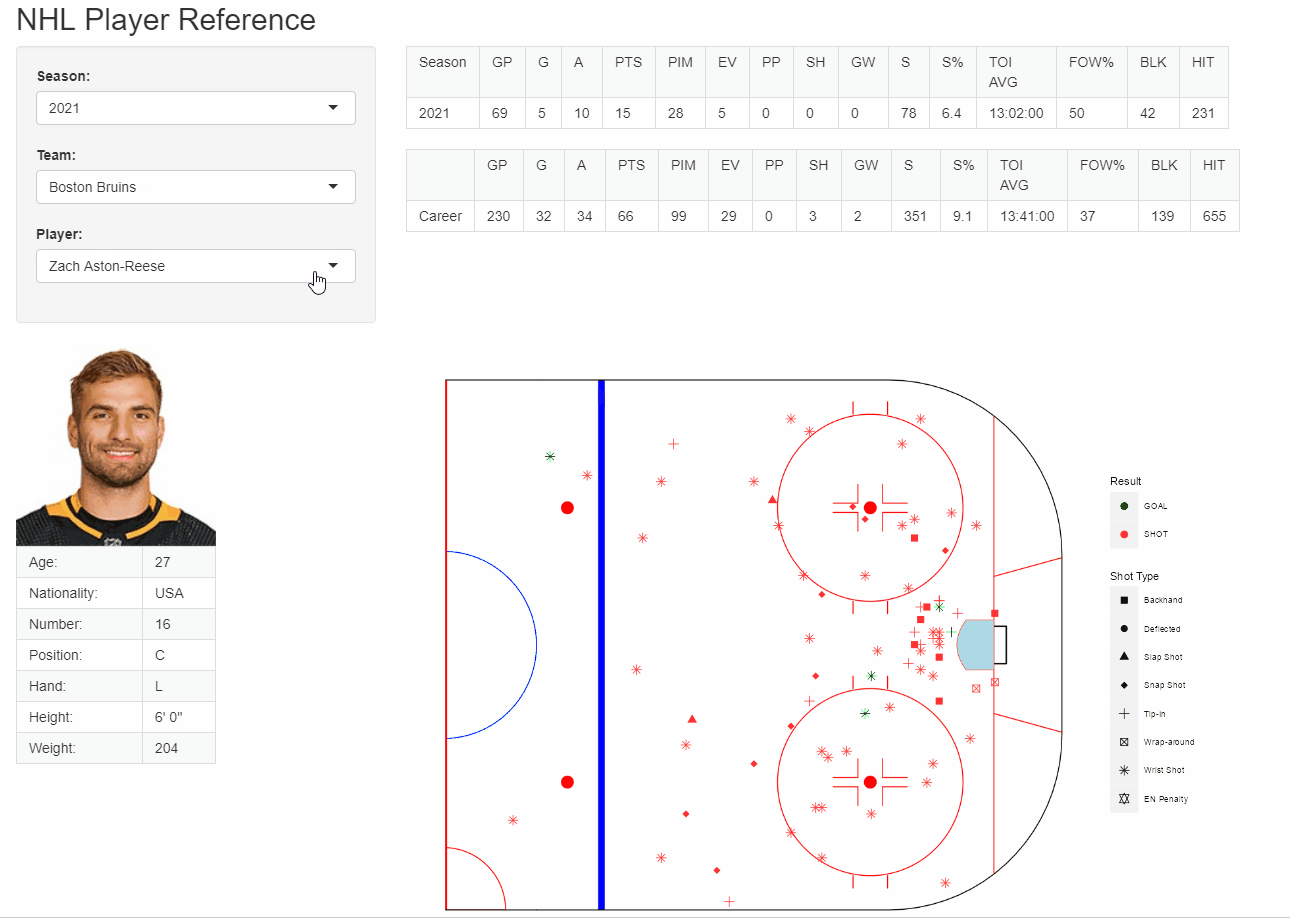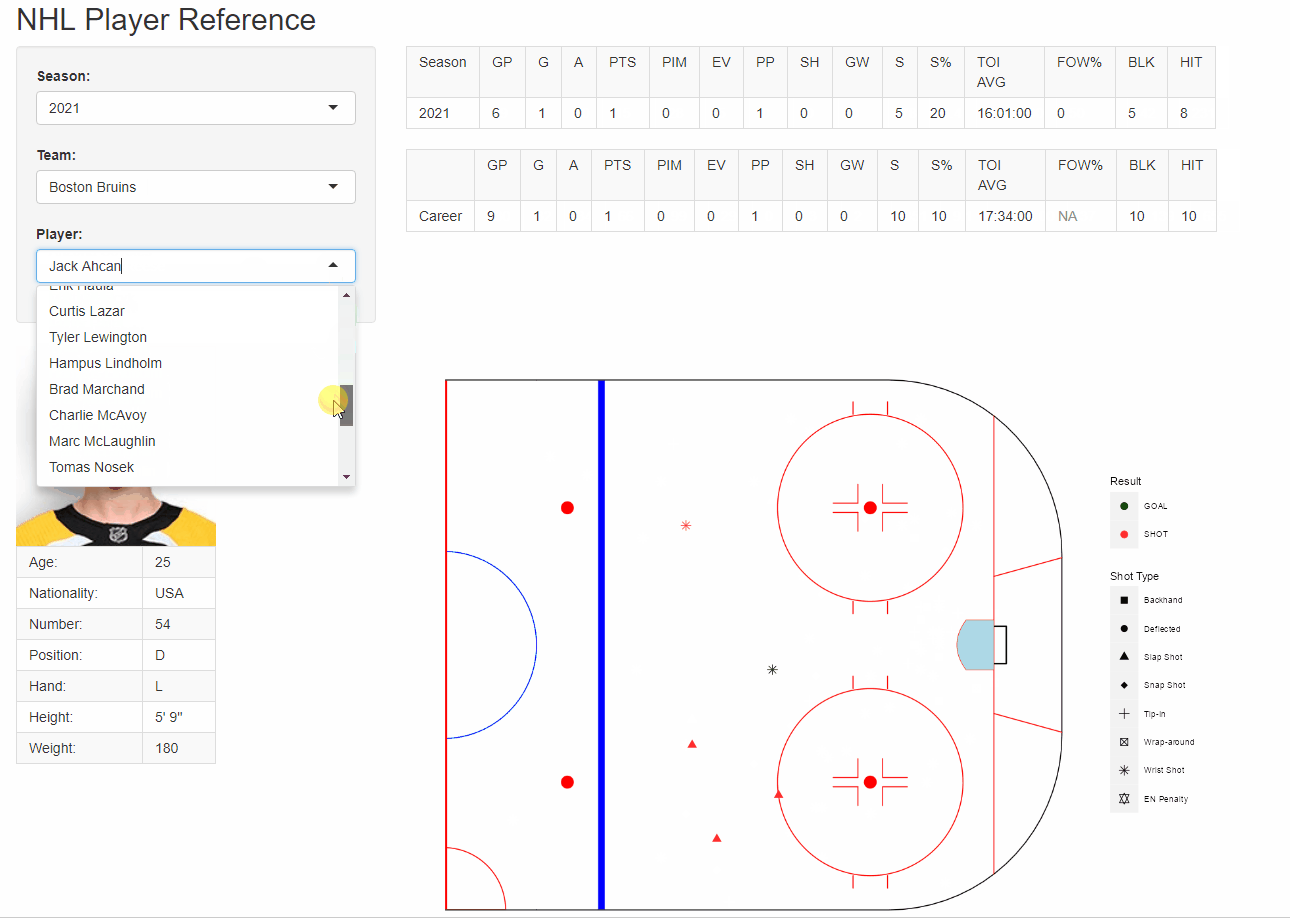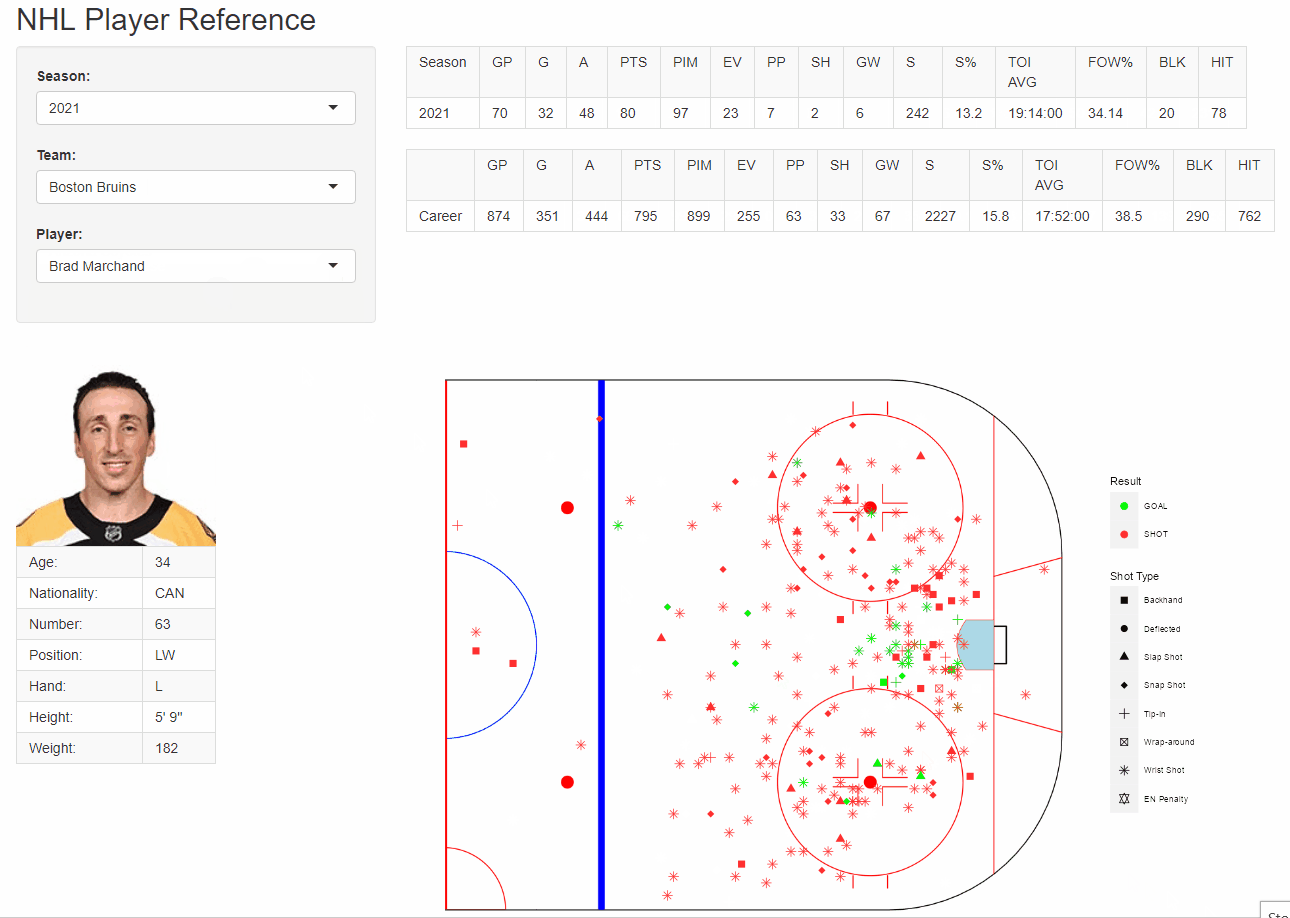 {fig.align = “center”}
{fig.align = “center”}
R
Note
This is a new language
Workflow
Before Class
Watch lecture content videos (will locate these during website tour)
Clone the application exercise (can be done right before class; we will practice this today)
During Class
Warm up question
Mix of lecture and live coding
Website
Course Website Tour
Slack Tour
Please bring your laptops if able
Activities and assessments
Homework: Individual assignments combining conceptual and computational skills.
Labs: Individual or team assignments focusing on computational skills.
Exams: Two take-home exams.
Final Project: Team project presented during the final exam period.
Application Exercises: Exercises worked on during the live lecture session.
Application Exercises
Are not graded for the first week
Turned in on GitHub (You will have this ability after Lab-0)
What is due is what we get through in-class
Lab
Run by TA Pritam Dey
Focus on computing using R tidyverse syntax
Apply concepts from lecture to case study scenarios
Work on labs individually or in teams of 3 - 4
Textbooks and readings
R for Data Science by Grolemund & Wickham (2nd ed. O’Reilly)
Introduction to Modern Statistics by Cetinkaya-Rundel & Hardin (1st ed. OpenIntro)
Questions?
Why learn the technology we do?
R + R-studio (Posit)
– Specialization in data visualization
– Computing tools to fit models
– Well respected
– You can take these skills with you
The language has grown significantly in popularity and is now used in a range of professions including software development, business analysis, statistical reporting and scientific research
Create a GitHub account (Why?)
GitHub, Inc., is an Internet hosting service for software development and version control. 
What we need to do (5 min)
– If you have not set up:
GitHub Account
Slack Account
Reserved a Duke Container
Create a GitHub account
Please do this before the Getting to know you survey
Go to https://github.com/, and create an account (unless you already have one).
Some tips from Happy Git with R.
– Incorporate your actual name!
– Reuse your username from other contexts if you can, e. g., Twitter or Slack.
– Pick a username you will be comfortable revealing to your future boss.
– Be as unique as possible in as few characters as possible. Shorter is better than longer.
– Avoid words with special meaning in programming (e.g. NA).
GitHub account
Invite Example
Slack

https://slack.com/get-started#/createnew
R-Studio
– Reserve a STA198-1991 RStudio container
– Go to https://cmgr.oit.duke.edu/containers
– Click Reserve Container for the STA198-199 container
To much talking…. let’s take a break (10 min)
Meet The Tool-Kit + Data Visualization
ae-01
– We will clone this from GitHub here: https://github.com/sta199-summer-1/ae-01-summer
– You will do this every day before class & with homework & with labs
– You will not have the capability to “push changes” to GitHub (yet… this will happen during your first lab!)
Cloning Demo
https://github.com/sta199-summer-1/ae-01-summer
R-Tour
Some R essentials
– Functions are (normally) verbs, followed by what they will be applied to in parentheses:

R essentials
– Packages are installed with the install.packages function and loaded with the library function, once per session.
– If you are using R through the container, almost all packages are already installed for you!

Packages
library(tidyverse)
Packages
library(tidyverse)

tidyverse

– The tidyverse is a collection of R packages designed for data science.
– All packages share an underlying philosophy and a common grammar.
Quarto
– an open-source scientific and technical publishing system
– publish high-quality articles, reports, presentations, websites, blogs, and books in HTML, PDF, MS Word, ePub, and more
– Code goes in chunks, defined by three backticks, narrative goes outside of chunks
How will we use Quarto?
– Every assignment / lab / project will be given to you as a Quarto document
– You will always have a Quarto template document to start with
– As we get more familiar with R, the more code you will construct on your own
ae-01
The process
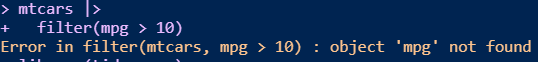
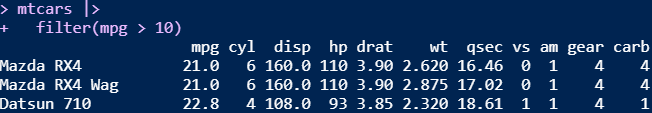
mtcars
You want to create a visualization. The first thing we need to do is set up the canvas…
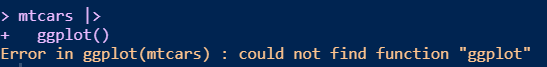
The process
mtcars |>
ggplot()

The process
mtcars |>
ggplot(
aes(
x = variable.name, y = variable.name)
)
aes: describe how variables in the data are mapped to your canvas
The process
+ “and”
When working with ggplot functions, we will add to our canvas using +
The process
mtcars |>
ggplot(
aes(
x = variable.name, y = variable.name)
) +
geom_point()
The process

Summary
– There area lot of moving parts in this course
– Coding is not learned in a day
– Ask questions often
– What is version control? Why is it important?
– What is R vs RStudio?
– What is Quarto?
– Starting to work with code!
